There are a lot of low voltage terms, abbreviations, and slang that can be quite intimidating to newcomers and outsiders. If you need a basic understanding of the low voltage industry -because of a project, contract, or job - this low voltage terms list will help you get started. We go from Analog to WAN and cover everything in between.
Before we start though we should cover, what is low voltage?
Low Voltage
Low voltage is classified as 50V (volts) or less. Low voltage will not cause a shock from contact. Commercial systems include security systems, sound and communication systems, LED lighting, and more.
All of the terminology listed below will relate to the field of low voltage. The list could go on for days if you’re into geek-speak, but we tried to cover only the essentials. Brush up on your low voltage terms and you’ll be able to have an informative and professional discussion about low voltage projects and systems.
Analog
Format that uses continuous physical parameters to transmit information. (Opposite: Digital)
Bandwidth
The information capacity of a cable, usually measured in GHz.
Broadband
Method of communication where the signal is transmitted by being impressed on a higher frequency carrier. Also, the ability of a communications system to carry several signals simultaneously.
CATV
(Cable TV) Uses coaxial or twisted pair cable, and recently optical fiber, to transmit signals from a service providers feed to multiple locations in a building.
Cat5
Ethernet cable that carries up to 155 Mbits over short distances. Has been superseded by Cat5E in most industries.
Cat5E
Ethernet cable standard that carries up to one gigabit per second.
Cat6
Next-generation Cat5E cable that supports gigabit network speeds but performs to a higher standard and minimizes interference and noise.
Cat6A
Newest North American recognized cable standard. Designed to support 10 gigabits per second.



CCTV
(Closed Circuit Television) Use of video cameras to transmit a signal to a single place
CMP
(Communications Multipurpose Cable, Plenum) Cable jacket fire-resistance rating, indicated that it’s suitable for a plenum space. Must pass a standardized flammability test and be certified by an accredited laboratory like UL.
CMR
(Communications Multipurpose Cable, Riser) Cable jacket fire-resistance rating, indicated that it’s suitable for a riser space. Must pass a standardized flammability test and be certified by an accredited laboratory like UL.
Coaxial Cable
Electrical cable used for high-frequency transmissions and broadband.
Conduit
A tube or pipe that cables are pulled through or housed.
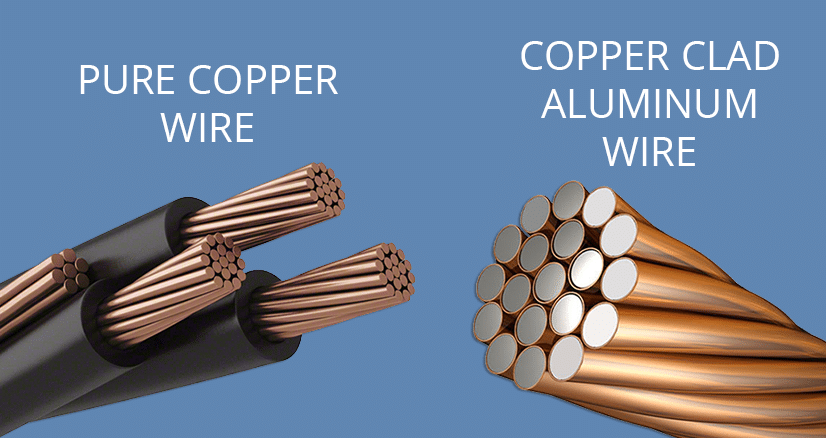
CCA
(Copper Clad Aluminum) Cables where the wire is made of aluminum and coated in copper. It is cheaper but performs poorly. Instead, look for 100% annealed pure copper wire.
DAS
(Distributed Antenna System) A way to deal with poor network coverage inside a building by installing small antennas throughout the area.
Digital
Data format that uses a discrete, countable, and a finite number of levels to transmit information. (Opposite: Analog)
Ethernet
Refers to the various computer networking technologies for a local area network.
EMI
(Electromagnetic Interference) Interference that causes degradation or failure.
Fiber Optic Cable
Very thin plastic or glass fiber wire made from pure optical glass, designed to use light to carry digital signals. It does not emit or receive EMI.
FTP
(Foiled Twisted Pair) Ethernet cable constructed with a single aluminum shield that surrounds all four pairs of wire inside the cable, helps prevent interference.
IDF
(Intermediate Distribution Frame) A free-standing or wall-mounted rack that interconnects cable, MDFs, and workstations.
IEC
(International Electrotechnical Commission) International, non-governmental organization that sets standards for electrical products.
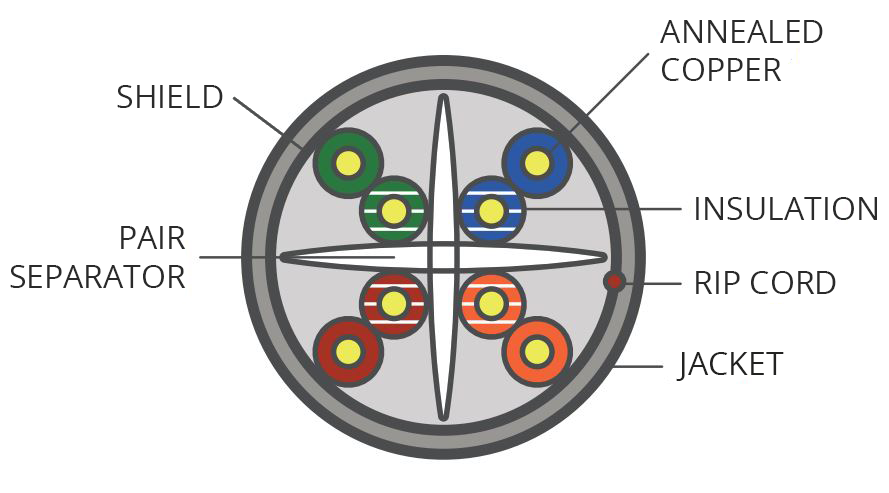
Insulated Wire
Covering a conductor with a non-conducting material, such as covering metal in plastic.
Jacket
External material covering a cable. Features information about flammability rating, temperature rating, manufacturer, etc.
LAN
(Local Aera Network) Limited data communications network for a small area like a home, office, or building.
LED
(Light Emitting Diode) Semiconductor diode that emits light when forward current is applied. Energy-efficient bulbs that can be powered over ethernet.
MDF
(Main Distribution Frame) Connects private or public lines coming into the building with the internal network. Interconnects with IDFs.
Modem
A device that carries out modulation and demodulation. The modem takes in digital information (0’s and 1’s) and sends it over a transmission medium.
MMF
(Multi-Mode Fiber) Allows multiple modes of light to propagate, allowing more data to pass through at a given time. This means the quality of the signal is reduced over long distances and is better suited to short-distance applications.
Network Cabling
Broad term referring to ethernet cabling structures for a building.
Non-Plenum
Cable that is run in non-plenum areas and rates as Riser.
Patch Panel
Distribution area to rearrange cable connections and circuits.
Plenum
Cable that is used in the plenum area of a building (where air circulates - air ducts, raised floors, etc.) without the need for conduit. The cable has a slow-burning, fire-resistant casing, and must not emit toxic smoke when exposed to fire and not reignite after self-extinguishing.
RJ45
Standard connector used for ethernet cables.
Riser
Cable that is used in non-plenum areas of a building (i.e., cable risers between floors, elevator shafts, etc.). The cable must still self-extinguish during a vertical burn test to prevent flames from traveling up the cable.
Shield
In a cable, it is a metallic layer placed around a conductor or group of conductors to prevent interference or signal leakage.
Splice
Permanent joining of fiber optic cables using heat to fuse or melt the ends.
STP
(Shielded Twisted Pair) Ethernet cable shielding where each individual pair of wires have their own aluminum shield.

Structured Cabling
Refers to the cabling infrastructure in a building. The background for all of the low-voltage technology.
Temperature Rating
Maximum/minimum temperature at which a cable will maintain its integrity without failing.
UL
(Underwriters Laboratories) An independent, non-profit product safety and certification organization. Products that do not follow the UL standards could pose serious fire risks and safety concerns.
UTP
(Unshielded Twisted Pair) Ethernet cables with no shield surrounding the twisted pair wires inside of the cable.
WAN
(Wide Area Network) A network that covers a broad geographical area.
Now that you're familiar with low voltage terminology, you need to get acquainted with the typical pricing structure. Download the Structured Cabling Purchasing Guidebook to learn about factors that influence cost, room types, and common cost factors for low voltage tech projects.
See any low voltage terms we’re missing? Comment below and let us know!



Leave a Comment